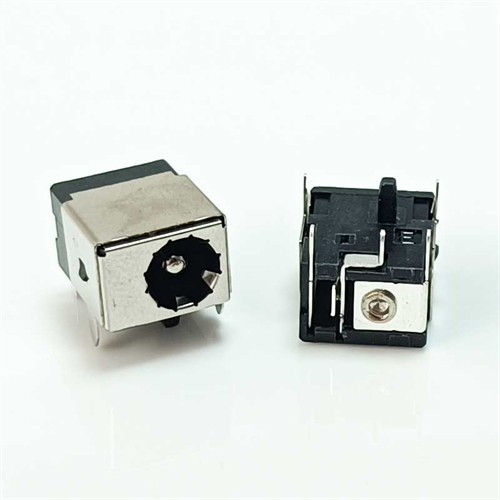
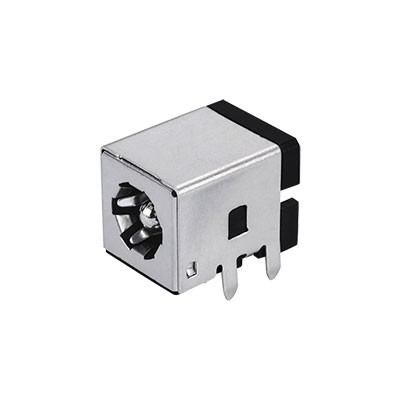
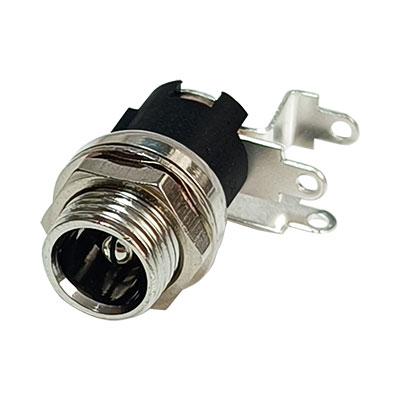
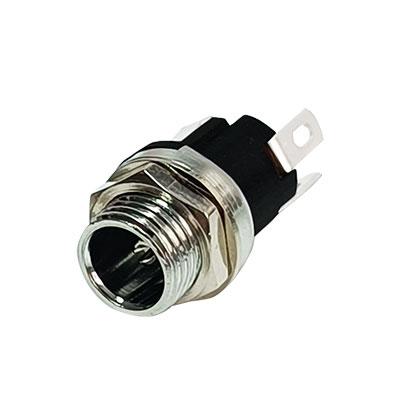
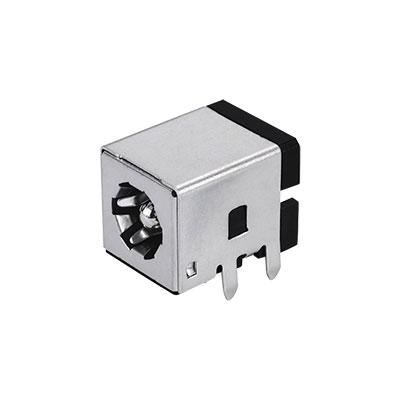
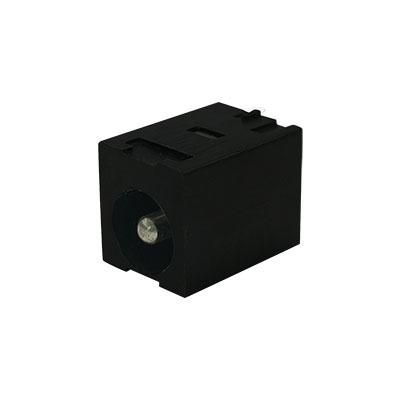
DC Jack Socket 2.0mm
DC Jack Socket (Solder) 2.5mm Pin
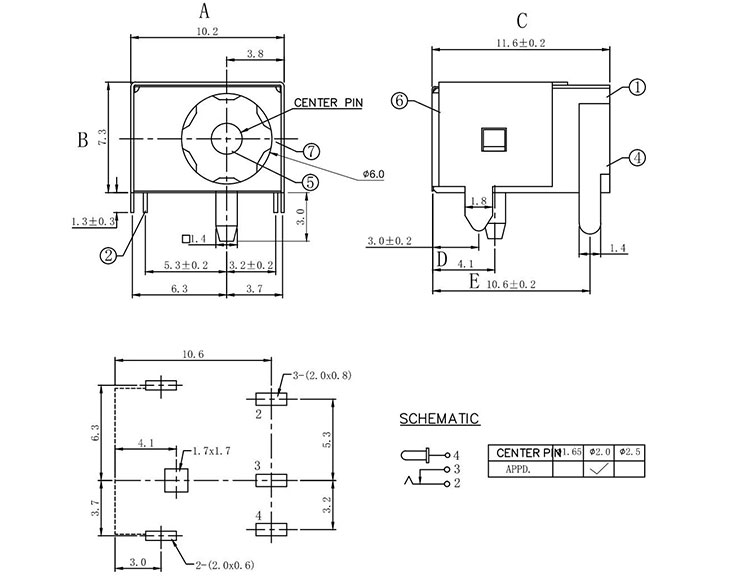
DC jack socket 2.0mm with screw for panel,High quality chassis mount DC jack socket to fit 8mm to 8.5mm panel cut outs. 3A 30V DC rating to suit most standard applications. This model features a centre pin 2.0mm diameter and internal diameter of 5.7mm. Complies with RoHS. Please download the drawing for full technical information.
A shielded DC power jack is a specialized type of power connector that offers enhanced protection and performance compared to standard DC power jacks. This description will cover its features, benefits, construction, and applications, highlighting why it's a crucial component in many electronic systems.
The shield of a DC power jack is typically made from a conductive material, such as metal (usually copper or aluminum). This metal shield encases the inner components of the jack, which include the positive and negative electrical contacts. The inner contacts are often made of highly conductive metals like brass, and they may be plated with materials like gold or silver to reduce electrical resistance and prevent oxidation.
The shield itself is usually connected to the ground or negative terminal of the power supply. This connection serves as a barrier, protecting the inner electrical contacts from external electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio - frequency interference (RFI). The outer metal casing of the shield can be integrated directly into the jack's body or added as an additional layer of protection. In some designs, the shield may be soldered or screwed onto the jack, ensuring a secure electrical connection.
Electromagnetic and radio - frequency interference are unwanted electrical signals that can disrupt the normal operation of electronic devices. These interferences can come from various sources, such as nearby electrical appliances, radio transmitters, or even the switching actions within other components of the same electronic system. The shield on the DC power jack acts as a Faraday cage. When an external electromagnetic field tries to penetrate the jack, the conductive shield redirects the interfering signals to the ground, preventing them from reaching the sensitive inner electrical contacts.
Similarly, when the DC power jack is part of a circuit that generates its own electromagnetic emissions, the shield helps contain these emissions within the jack, reducing the likelihood of the device interfering with other nearby electronics. This bidirectional protection is essential for maintaining the integrity of the power signal and ensuring the stable operation of the connected electronic device.
INQUIRY
CATEGORIES
LATEST NEWS
CONTACT US
Contact: Bella
Phone: 15999819066
E-mail: rucoe@rucoe.com
Whatsapp:+86-15999819066
Add: Taoyuan Street, Nanshan, Shenzhen